Satellites Face Growing Security Risks from Russia and China with Over 10,000 Incidents Per Year: Experts Urge Shift Toward Laser-Based Space Communication
Vilnius, Lithuania, May 5, 2025 – A new 316-page report released by the Secure World Foundation reveals a growing global race to develop counterspace capabilities. Russia and China are leading a surge in tactics that include jamming, spoofing, and cyber interference targeting satellites like Starlink.
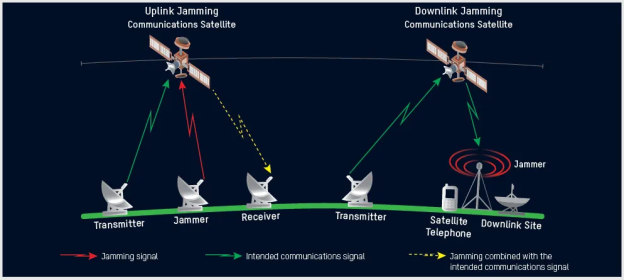 |
| An illustration depicting how uplink and downlink jamming occurs (Source: Defense Intelligence Agency) |
The report assesses 12 countries’ counterspace programs and finds increasing overlap between commercial satellite infrastructure and military use. It proves a rising concern about the security of radio frequency (RF)-based systems.
The 2025 edition of the “Global Counterspace Capabilities” report covers developments from February 2024 to February 2025 and documents over 10,000 satellite interference events. Many of them have occurred in areas of active conflict, including Ukraine, Syria, and the Middle East.
Russia has been singled out for its GPS jamming of civilian aircraft and Starlink signals in Ukraine. China, meanwhile, is investing in sophisticated cyber tools and even co-orbital ASAT (anti-satellite) capabilities, using its expanding fleet of inspector satellites.
“Satellite infrastructure is no longer just commercial, but strategic. Space has become a new front line, and the systems we rely on are increasingly being pulled into geopolitical conflict. However, the vulnerabilities in current systems stem from old technology. RF-based communication is easily jammed, intercepted, and spoofed. That is not only technical, but even more so, a systemic risk,” said Laurynas Mačiulis, CEO of Astrolight, a Lithuanian space-tech company dedicated to facilitating laser communications.
Laser communication, or free-space optical communication, is gaining attention as a more secure alternative. It uses tightly focused beams of light to transfer data. Therefore, it is more difficult to jam, tap, or intercept, according to Mačiulis.
The dual-use nature of these technologies suggests that these countries are not only preparing to interfere with RF-based systems but also potentially positioning themselves to exploit more secure, laser-based infrastructure in the future.
“We’ve spent decades relying on RF systems because they were the only viable option. But now, with the demands of modern satellite networks and real threats covered in the report, we need a system upgrade. What’s at stake is the safety of people who depend on satellites every day,” added Mačiulis.
The Secure World Foundation report also warns that as militarization moves to space, everyday services such as airlines, logistics networks, and civilians in conflict zones become collateral damage.
Astrolight’s work focuses on solving one of the most under-addressed gaps in space lasercom: secure, high-speed laser communication between space and Earth. While satellite-to-satellite optical links are bringing tremendous improvements in resilience and throughput of space-based networks (such as in Starlink’s newer generations), the final leg, which is exchanging data securely with Earth, remains constrained by limitations of RF technology, such as low bandwidth and vulnerability to interference.
The main challenge of implementing space-to-Earth optical links is that it can be affected by weather or cloud coverage. Site diversity and interoperability of terrestrial and in-space optical communication networks are the key to solving this problem, according to Mačiulis.
“Laser communication benefits not only space, but also ground operations,” Mačiulis noted. “In case the war breaks out, our neighbouring Baltic Sea could become the battlefield. In that case, the victory in electronic warfare would rely heavily on who has the upper hand in terms of secure information sharing.”
For maritime needs, the company introduced POLARIS, a lasercom system designed with the Lithuanian Navy, and now considered for broader use by other NATO Navies to replace vulnerable signal lamps.
“We can’t afford to wait for a catastrophic outage to rethink how we communicate in space. “We’ve got the tools. Now it’s about implementing them before it’s too late,” concluded Mačiulis.
About Astrolight
Founded in 2019 by an ex-founder and CTO of Kongsberg Nanoavionics, Laurynas Mačiulis, together with co-founders from leading European laser companies, Astrolight is on a mission to bridge the connectivity gap between space and Earth by leveraging laser communication. Astrolight laser communication terminal ATLAS stands out from competitors due to its small size and low power consumption, leveraging Astrolight’s proprietary beam steering and modular optical amplifier system design.





